-
Whatsapp: +86-13681923533
-
email: jminfo@jm-industry.com
How to Detect Surface Cracks in Fasteners: 4 Critical NDT Methods Explained
Jul 31, 2025
Why Crack Detection Matters
Surface cracks in bolts, screws, and studs reduce load capacity by up to 90% and cause 80% of fastener failures in critical applications. This guide covers industry-proven NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) methods to identify defects before they compromise structural integrity.
The 4 Core Crack Detection Methods
(Selection Depends on Material & Defect Type)
| Method | Best For | Detection Limit | Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Particle (MT) | Ferromagnetic fasteners | 0.1 μm | ★★★★★ | $$ |
| Liquid Penetrant (PT) | Non-magnetic metals | 0.5 μm | ★★★☆☆ | $ |
| Ultrasonic (UT) | Internal/sub-surface defects | 0.1 mm | ★★☆☆☆ | $$$$ |
| Visual Inspection (VI) | Quick field screening | 0.1 mm | ★★★★★ | $ |
1. Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): For Steel Fasteners

How It Works
-
Magnetize fastener → Crack disrupts magnetic field → Magnetic particles cluster at defect
-
UV light reveals fluorescent particle patterns
Optimal Use Cases
-
Carbon/alloy steel bolts (Grade 5/8, A325)
-
Head-to-shank fillet areas
-
Thread root cracks
JM Hardware® Pro Tip:
*"For high-strength bolts >10.9 grade, use DC magnetization. AC won't detect subsurface flaws."*
2. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): Universal Surface Checks
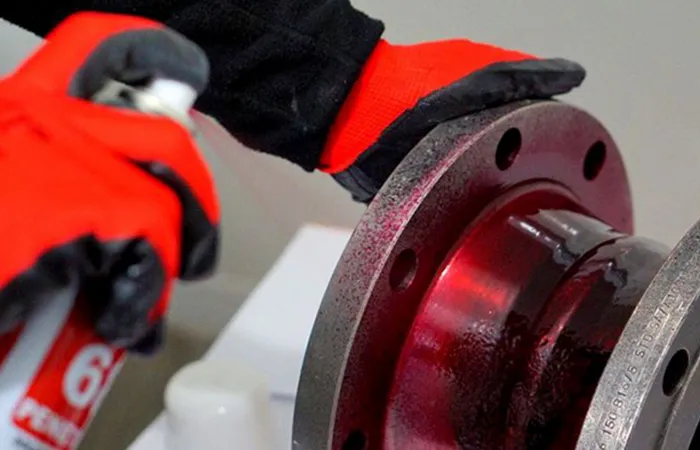

4-Step Process
-
Clean: Remove oil/grease (ASTM E165)
-
Penetrant: Apply red dye/fluorescent fluid (5-30 min dwell)
-
Developer: Draw out penetrant from cracks
-
Inspect: Under white/UV light
Ideal For
-
Stainless steel fasteners (A193 B8)
-
Complex geometries (e.g., socket heads)
-
Field inspections
Limitation Alert: Cannot detect sealed or subsurface defects.
3. Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Deep Defect Detection
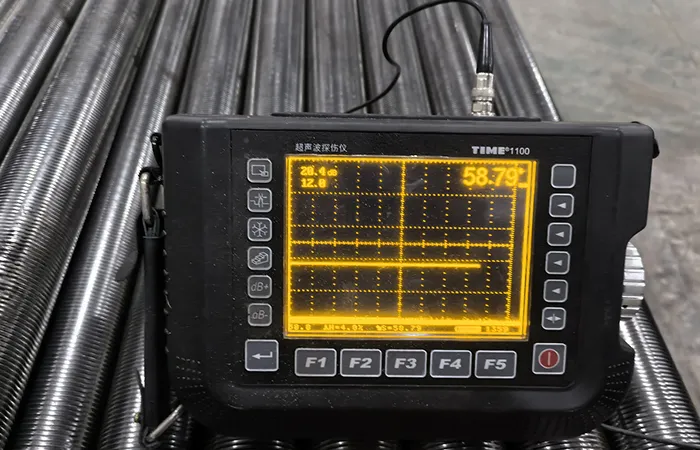

Technical Procedure
-
Transducer sends 1-10 MHz sound waves
-
Crack reflection creates echo patterns
-
Time-of-flight calculates depth
Critical Applications
-
Anchor bolts in concrete
-
Large-diameter flange studs
-
Aerospace fasteners (NASM specs)
Data You Get:
✓ Crack depth ✓ Orientation ✓ Length
4. Visual Inspection (VI): First Line of Defense
Enhanced Techniques
| Tool | Magnification | Smallest Detectable Crack |
|---|---|---|
| Naked eye | 1× | 0.5 mm |
| 10x Loupe | 10× | 0.1 mm |
| Digital Microscope | 200× | 5 μm |
Inspection Zones to Target:
-
Under bolt heads
-
Thread run-out sections
-
Stress-corrosion prone areas
Method Selection Guide: Match Technique to Need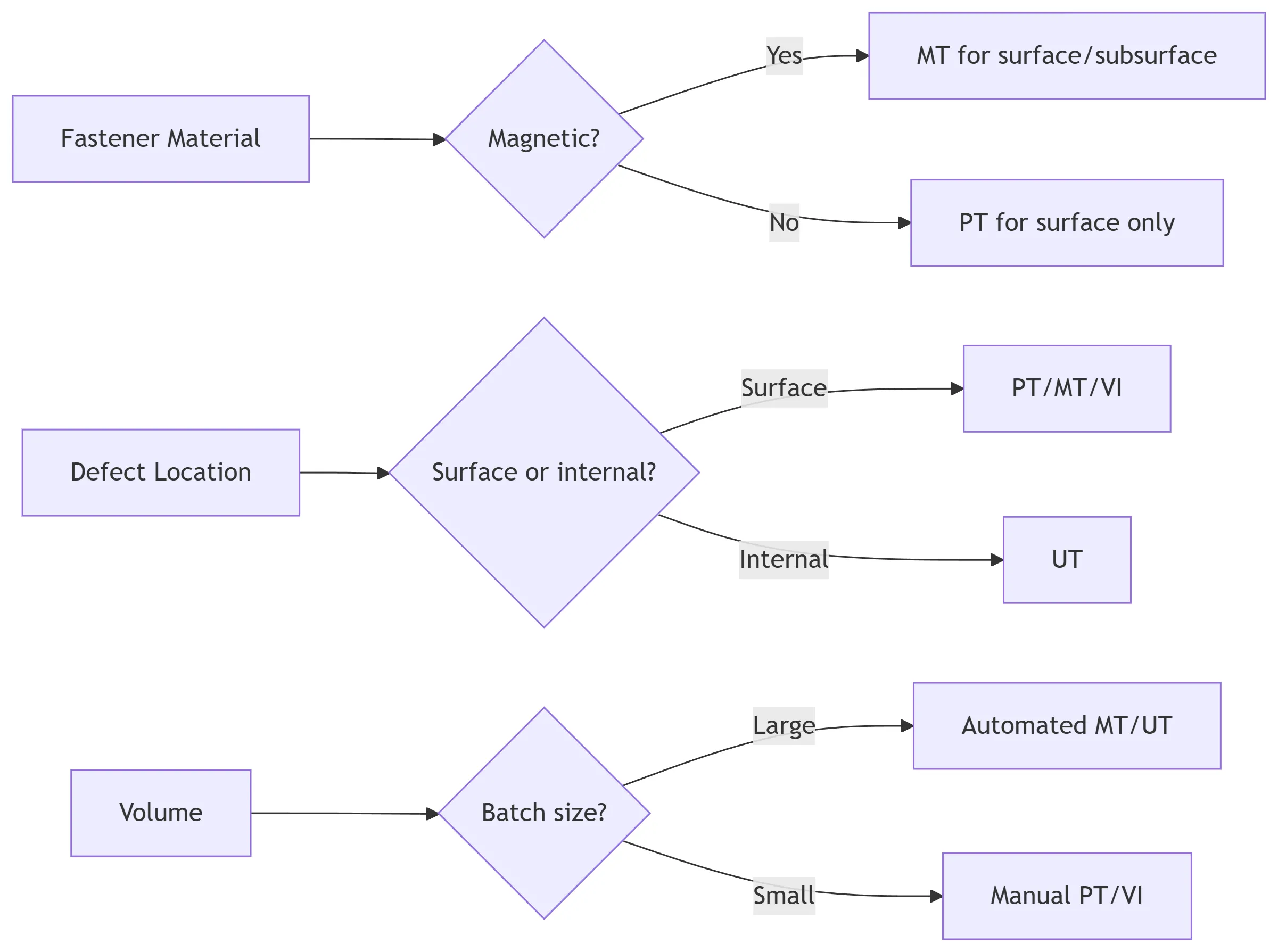
Why Trust JM Hardware® Fasteners?
We implement 3-layer quality assurance:
-
Raw Material Scan: PMI (Positive Material Identification)
-
Process Control: Inline UT during cold forging
-
Final Verification: 100% MT for ferromagnetic fasteners
Certifications: ISO 9018, ASTM E1444/E1417, NADCAP AC7114
Request Our Inspection Reports:
✉️ Email: jminfo@jm-industry.com
📱 WhatsApp: +8613681923533 -
Recent Posts

October 26, 2016
The Most Successful Engineering Contractor


.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_100/quality,q_100)
